Noise pollution has become an increasingly prevalent issue in our modern society, and its effects on our overall well-being should not be underestimated. One area particularly susceptible to the negative consequences of noise pollution is our hearing health. Prolonged exposure to loud sounds can have a significant impact on our auditory system, leading to hearing loss, tinnitus, and other hearing-related problems. In this article, we will explore the impact of noise pollution on hearing health and discuss ways to protect our ears from its harmful effects.
- Understanding Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is a type of hearing impairment caused by exposure to loud sounds. When we are exposed to excessive noise levels, the delicate structures in our ears can be damaged, leading to irreversible hearing loss. NIHL can occur gradually over time with repeated exposure to loud noises, or it can result from a single intense noise event. Occupational noise, recreational activities (such as attending concerts or using loud power tools), and environmental noise are common sources of noise pollution that can contribute to hearing loss.
- The Role of Decibel Levels: The intensity of sound is measured in decibels (dB), and prolonged exposure to sounds above 85 dB can be harmful to our hearing. For reference, normal conversation typically ranges between 60-70 dB, while a rock concert or a busy city street can reach levels of 100 dB or higher. It’s important to note that the duration of exposure also plays a role. Even sounds at lower decibel levels can cause damage if experienced for an extended period. Therefore, it’s crucial to be aware of the noise levels in our environment and take appropriate precautions.
- Effects on Tinnitus: Tinnitus is the perception of ringing, buzzing, or other sounds in the ears without any external source. Exposure to loud noises is a common cause of tinnitus. Prolonged exposure to noise pollution can increase the risk of developing chronic tinnitus. The persistent nature of tinnitus can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, causing sleep disturbances, difficulty concentrating, and emotional distress. Protecting our ears from excessive noise can help reduce the risk of tinnitus.
- Protective Measures: To safeguard our hearing health from the detrimental effects of noise pollution, it’s essential to adopt protective measures. Here are some practical steps we can take:
- Use earplugs or earmuffs in loud environments, such as concerts, construction sites, or sporting events.
- Limit the duration and volume of exposure to loud sounds. Take regular breaks from noisy environments and use volume-limiting headphones or earbuds when listening to music or watching videos.
- Maintain a safe distance from sources of loud noise, such as speakers, machinery, or heavy traffic.
- Create a quiet and peaceful environment at home by using soundproofing techniques, such as installing double-pane windows or adding sound-absorbing materials.
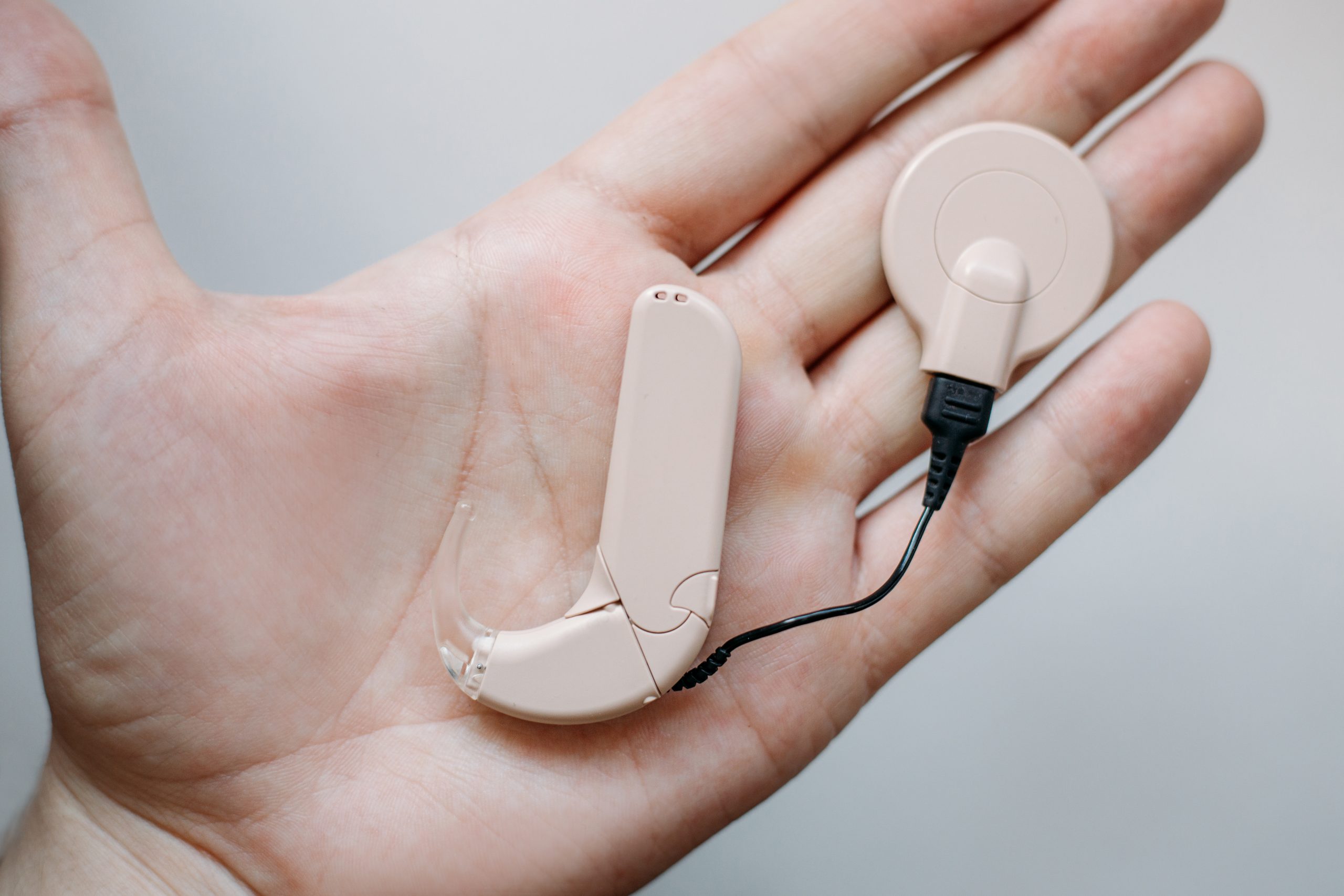
- Hearing Protection for Specific Groups: Certain individuals may be more vulnerable to the effects of noise pollution. This includes workers in industries with high noise exposure, musicians, and individuals with pre-existing hearing conditions. For these individuals, using specialized hearing protection devices, such as custom-made earplugs or earmolds, can provide an extra layer of protection.
6. Awareness and Advocacy: Raising awareness about the impact of noise pollution on hearing health is crucial. Encouraging local authorities to enforce noise regulations, promoting public education about the importance of hearing protection, and supporting initiatives to reduce noise pollution can help create a healthier acoustic environment for everyone.
In conclusion, noise pollution can have a significant impact on our hearing health, leading to hearing loss, tinnitus, and other auditory problems. Protecting our ears from excessive noise levels is vital to prevent these issues